A Division of the Hoskin Group, Canada's Instrumentation Leader


Mining Measurement Solutions Built for Extreme Conditions
Mining is the extraction of valuable minerals or other geological materials from the earth, usually from an ore body, vein or (coal) seam. Materials recovered by mining include base metals, precious metals, iron, uranium, coal, diamonds, limestone, oil shale, rock salt and potash. Heavy machinery is a common application for sensor technology.
Mining Measurement Solutions Built for Extreme Conditions Products:
Mining Measurement Solutions Built for Extreme Conditions

TE 64X Crash Test Accelerometer
The TE Connectivity model 64X is the most advanced accelerometer ever released for anthropomorphic dummy instrumentation. The accelerometer features a full bridge output configuration with ideal gas damping tailored for outstanding shock survivability and a flat frequency response to >8kHz. The model 64X accelerometer has a standard cross-talk accuracy of
TE 13201A (single axis) and 23201A (dual axis) Accelerometer
The TE Connectivity model 13201A and 23201A accelerometers are rugged analog accelerometers capable of accurately measuring vibration inputs along each axis. The model 13201A sensor is a single axis accelerometer while the model 23201A is a dual axis accelerometer and both include a temperature sensor output. The 13201A & 23201A
QuantumX MXFS BraggMETER Optical Interrogator
QuantumX MXFS: Integrating Optical and Electrical Measurements into One Reliable System QuantumX MXFS makes optical measurements easy, flexible and competitive – up to your needs. It brings you all the optical benefits of the filter based BraggMETER technology: measuring a large sensing network composed by various types of sensors, high
JDI Series – Digital MEMS Inclinometer
The JDI-100/200 series is a digitally temperature compensated inclinometer available in single and dual axis configurations. The robust and rugged design is great for industrial use, yet includes the low-cost MEMS technology. These units are available with DB9, Pigtail, Deutsch, Double Deutsch, 6-Pin Circular (C06), or M12 connectors for maximum
T40MS – Torque Flange
T40MS Torque Transducer: from 500 Nm to 2 kNm at 25,000 rpm T40MS is outstanding for its precision, reproducibility and robustness and is particularly well-suited for static and dynamic torque measurement. The torque transducer features 0.03% accuracy in terms of linearity including hysteresis, as well as high temperature stability. Combined
AR100 Laser Displacement Sensor
The AR100 is one of the smallest laser displacement sensors in the world. The ultra-compact AR100 comes with ranges from 10mm (0.4 in.) to 500mm (19.7 in.) with a single case size. It can take 9,400 measurements per second and has a linearity of ± 0.05% of the full measurement
SomatXR MX471C-R Ultra-Rugged CANbus FD Module
The SomatXR MX471-R CAN bus module allows the simultaneous integration of up to four CAN networks into the SomatXR data acquisition system. This module is the more rugged version of the QuantumX MX471 and is ideal for use in extremely tough conditions, such as vehicle tests in the field and
QuantumX MX471C CANbus FD module
CAN bus Module for Easy Integration of up to 4 CAN Networks The QuantumX MX471 CAN bus module allows the simultaneous integration of up to four CAN networks into the QuantumX data acquisition system and can be expanded as required. The module, combined with analog measurement modules, is ideally suited
TFX-5000 Ultrasonic Clamp-on Flow Meter
TFX-5000 ultrasonic clamp-on meters are quickly and easily installed without cutting or tapping the pipe. Ultrasonic waves transmit upstream and downstream through the pipe wall and water flowing in the pipes. By measuring the difference in the travel time and knowing the pipe size, the meter determines the velocity and flow
Type 1056 DC Static Centering Unit
Compatible with the entire range of Brüel & Kjær modal exciters, this unit serves two different purposes depending on which exciter is connected. When paired with Type 4827 or 4828, the unit provides variable stiffness to the armature suspension and correctly centres the armature in relation to both the exciter’s
Types 4827 And 4828 Modal Exciter
The most powerful of our modal exciters, Types 4827 and 4828 offer precise and reliable operation in any modal testing scenario, including long-duration tests of outsized mechanical structures as well as applications with MISO and MISO configurations. Suitable for impulse, sine and random signals, they also have a wide frequency
Types 4825 And 4826 Modal Exciter
As light and compact as Type 4824, these modal exciters are much more powerful. They combine a wide frequency range (DC – 5000 Hz) and up to 25.4 mm (1 in) of displacement for improved performance at low frequencies. Suitable for impulse, sine and random signals, Types 4825 and 4826
Type 4824 Modal Exciter
Powerful despite its small dimensions, Type 4824 is built to offer versatility and reliability in challenging modal applications, including SISO and SIMO tests of mechanical components, such as engines, as well as MISO and MISO tests of large structures. Suitable for impulse, sine and random signals, it also features a
LDS Comet USB Vibration Controller
The LDS® COMETUSB™ controller has been designed to offer an affordable and flexible solution for basic vibration testing needs. It is used in R&D and production test applications, such as stress screening. Its test profiles include random, sine, and shock excitations. It combines 24-bit precision with a wide dynamic control range and
LDS Laser USB Vibration Controller
Designed to generate a shaker drive signal and perform data measurements, the LDS® LASERUSB™ controller is typically used in R&D and production test applications, such as simulation of vibration and fatigue tests for automobiles, military vehicles, and ground transportation. It combines 24-bit precision with a wide dynamic control range and fast loop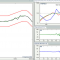
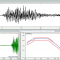
Shock Response Spectrum Synthesis Vibration Control
SRS synthesis is used to evaluate the shock resistance of the DUT (device under test). This is achieved by synthesizing, within a closed-looped test system, a user-specified SRS profile of acceleration versus frequency in order to create complex transient waveforms for driving an electrodynamic shaker. The desired SRS profile is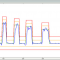
Random-On-Random Vibration Control
Random-on-random (RoR) control simulates real-world complex vibration environments with a combination of a broadband random signal and one or more superimposed random narrow-bands. Both signal types are usually present simultaneously and the narrow-bands can appear at fixed frequencies or sweep over a predefined range. The overall random PSD (power spectral
Sine-On-Random Vibration Control
Sine-on-random (SoR) control simulates complex vibration environments with a combination of broadband random excitation and sinusoids or 'tones'. Generally, both signal types are present simultaneously and the tones may either appear at fixed frequencies or sweep over a frequency range. A typical example is the vibration from an automobile drive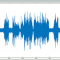
Time Waveform Replication Vibration Control
Time waveform replication (TWR), also known as long time history (LTH), exactly replicates, in the laboratory, vibration environments using data obtained in the field. Field measurements, such as a vehicle’s road test or an aircraft flight run, can be imported into the host PC, compensated for suitability to the shaker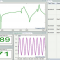
Resonance Search, Track And Dwell Vibration Control
Resonance search, track and dwell (RSTD) is an invaluable test for automated fatigue testing. A sine sweep is used to detect the resonant frequencies of the device under test (DUT). The test then dwells upon these frequencies for a specified period or number of cycles, automatically tracking changes in resonance